what would happen to the earth without the greenhouse effect
Earth'south climate is changing rapidly. We know this from billions of observations, documented in thousands of journal papers and texts and summarized every few years by the United nations' Intergovernmental Console on Climate change. The primary cause of that change is the release of carbon dioxide from burning coal, oil and natural gas.
International climate talks in Lima this calendar week are laying the foundation for next yr's UN climate summit in Paris. While negotiations well-nigh reducing emissions grind on, how much warming are nosotros already locked into? If we stop emitting greenhouse gases tomorrow, why would the temperature continue to rise?
Basics of carbon and climate
The carbon dioxide that accumulates in the atmosphere insulates the surface of the Globe. It'due south similar a warming blanket that holds in oestrus. This energy increases the Earth'southward surface average temperature, heats the oceans and melts polar water ice. Equally consequences, sea level rises and weather changes.
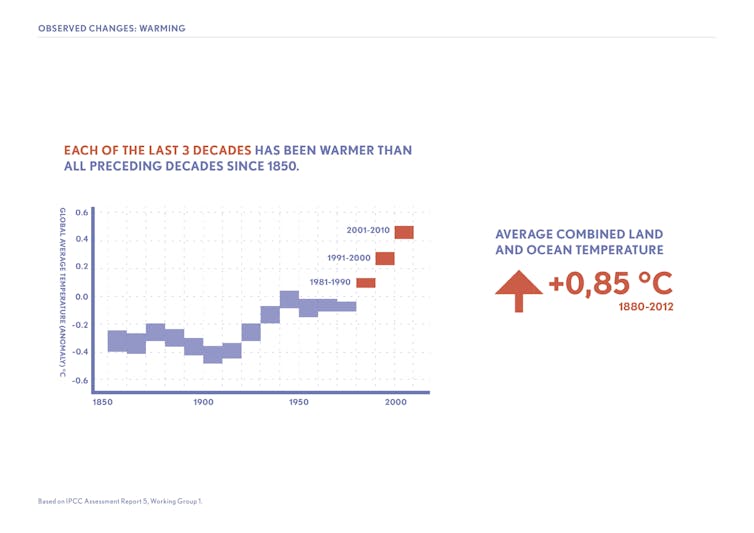
Since 1880, after carbon dioxide emissions took off with the Industrial Revolution, the average global temperature has increased about one.5F (0.85C). Each of the last three decades has been warmer than the preceding decade, besides every bit warmer than the entire previous century.
The Arctic is warming much faster than the average global temperature; ice in the Arctic Ocean is melting and the permafrost is thawing. Ice sheets in both the Arctic and Antarctic are melting. Ecosystems on both land and in the bounding main are irresolute. The observed changes are coherent and consistent with our theoretical understanding of the World's energy balance and simulations from models that are used to understand past variability and to assistance us call back nigh the futurity.

Slam on the climate brakes
What would happen to the climate if we were to stop emitting carbon dioxide today, right at present? Would we return to the climate of our elders? The elementary answer is no. In one case we release the carbon dioxide stored in the fossil fuels we fire, it accumulates in and moves amongst the atmosphere, the oceans, the state, and the plants and animals of the biosphere. The released carbon dioxide volition remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years. Merely after many millennia will it return to rocks, for example, through the formation of calcium carbonate – limestone – every bit marine organisms' shells settle to the bottom of the ocean. Simply on fourth dimension spans relevant to humans, once released the carbon dioxide is in our environs essentially forever. It does not become away, unless we, ourselves, remove it.
If we stop emitting today, it's not the stop of the story for global warming. In that location's a delay in temperature increase every bit the climate catches up with all the carbon that's in the temper. Subsequently maybe 40 more years, the climate volition stabilize at a temperature higher than what was normal for previous generations.
This decades-long lag betwixt cause and effect is due to the long time it takes to oestrus the ocean'south huge mass. The energy that is held at the Earth by the increased carbon dioxide does more than oestrus the air. It melts ice; it heats the ocean. Compared to air, it's harder to raise the temperature of h2o – it takes fourth dimension, decades. Yet, in one case the ocean temperature is elevated, it adds to the warming of the Earth'south surface.
And then even if carbon emissions stopped completely right now, as the oceans catch upwards with the temper, the Earth's temperature would rise almost some other 1.1F (0.6C). Scientists refer to this as committed warming. Water ice, also responding to increasing heat in the body of water, will continue to cook. There's already disarming show that significant glaciers in the West Antarctic water ice sheets are lost. Ice, h2o, and air – the actress estrus held on the Earth by carbon dioxide affects them all. That which has melted will stay melted – and more will melt.
Ecosystems are altered by natural and manmade occurrences. As they recover, it will be in a different climate from that in which they evolved. The climate in which they recover will non be stable; it will exist continuing to warm. There will be no new normal, only more than modify.
All-time of the worst example scenarios
In any event, it'south not possible to finish emitting carbon dioxide today, right now. Despite significant advances in renewable energy sources, total demand for energy accelerates and carbon dioxide emissions increase. I teach my students that they demand to plan for a globe 7F (4C) warmer. A 2011 study from the International Energy Agency states that if we don't go off our current path, so we're looking at an World 11F (6C) warmer. Our current Earth is just over 1F warmer, and the observed changes are already disturbing.
There are many reasons that we need to essentially eliminate our carbon dioxide emissions. The climate is irresolute apace; if that stride is slowed, the affairs of nature and homo beings tin can suit more readily. The total corporeality of modify, including bounding main-level rise, can be limited. The further we get away from the climate that we accept known, the more unreliable the guidance from our models and the less probable we will be able to ready. The warmer the planet gets, the more probable reservoirs of carbon dioxide and methane, another greenhouse gas that warms the planet, will be released from storage in the frozen Arctic permafrost – farther adding to the problem.
If nosotros terminate our emissions today, we won't go back to the past. This is non reason, however, to continue with unbridled emissions. We are adaptable creatures, with credible noesis of our climate'due south future and how we can frame that future. We're already stuck with some amount of guaranteed climate change at this point. Rather than trying to recover the past, nosotros need to be thinking about best possible futures.
Source: https://theconversation.com/what-would-happen-to-the-climate-if-we-stopped-emitting-greenhouse-gases-today-35011
0 Response to "what would happen to the earth without the greenhouse effect"
Post a Comment